Car.MLV.ai~Autonomous Vehicle
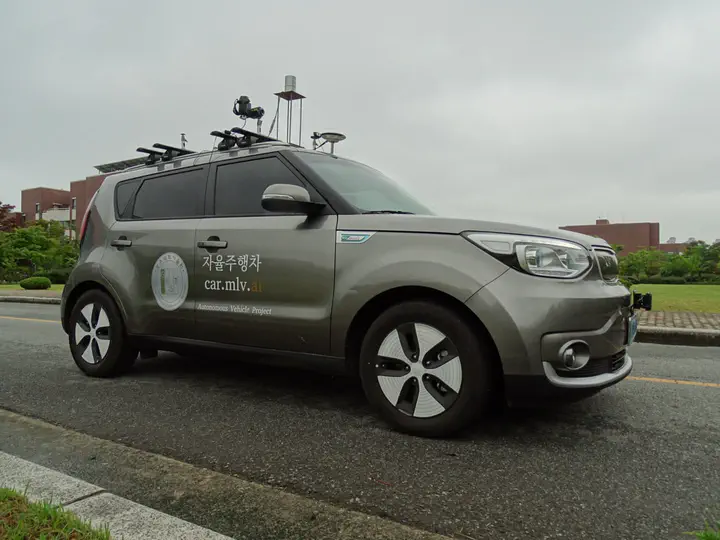 Photo by Micheal Basford
Photo by Micheal Basford
In this study, we have developed an autonomous vehicle using limited sensor suite as compared to autonomous vehicles discussed previously. Figure illustrates our test-bed called Car.Mlv.ai. The efficacy of our autonomous vehicle is experimentally verified by deploying it as an automated taxi service in the constrained environment. The proposed autonomous vehicle is composed of localization, perception, planning and control modules. The design of a distributed system and incorporation of robust algorithms enable the autonomous vehicle to perform efficiently. The fusion of sensor data for localization in map generation and navigation and also in perception module enable reliable object detection, recognition and classification in a dynamic environment. In the planning module, the optimal path is devised by considering the lane, obstacle information, and upon which velocity and behaviour planning are executed. Finally, based on the planning results, the control module performs the lateral and longitudinal control of the autonomous vehicle.
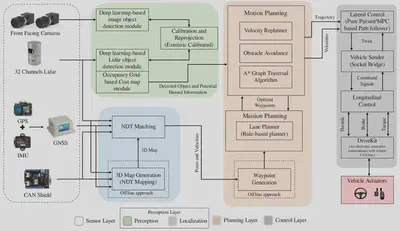
The architecture of the autonomous vehicle is composed of four major layers, as illustrated in Figure above, that are sensor layer, perception layer, planning layer and control layer. The sensor layer constitutes of exteroceptive and proprioceptive sensor modalities which provide the data to the different layer’s modules. In the perception layer, the two main elements that contribute toward the environment understanding are detection and localization. The understanding of the environment in the perception layer provides the necessary information to the planning layer. The planning layer devises the motion, mission and trajectory planning of the autonomous vehicle based on the observation accumulated in the perception layer. The decision from the planning layer is fed to the control layer for the execution of the control command to vehicle actuators through the lateral and longitudinal controller. The following subsections describe the modules used in perception, planning and control layers for the autonomous vehicle.
The demonstration video of the project.
Demo of Avoiding the dog. Demo of Obstacle Stopping at the Entrance or Exit Gate Barrier. Demo of Obstacle Stopping upon detection pedestrain. Driving in the campus. Demo of Obstacle Detection using RGB and Thermal Camera and Projection in the Lidar Frame. News coverage of our project sponsored by GIST.