Exploring thermal images for object detection in underexposure regions for autonomous driving
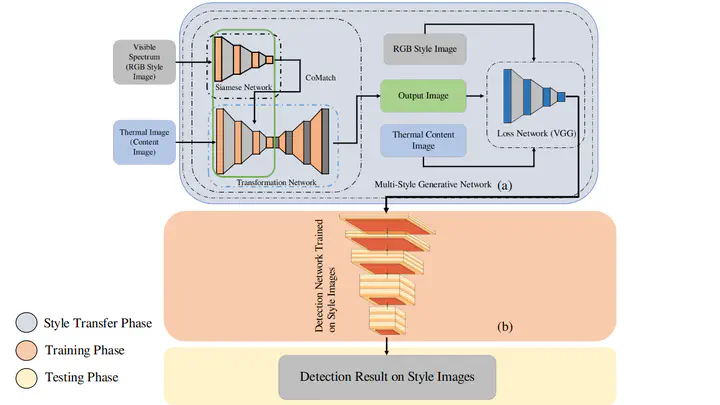 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
Underexposure regions are vital in constructing a complete perception of the surrounding environment for safe autonomous driving. The availability of thermal cameras has provided an essential alternative to explore regions where other optical sensors lack in capturing interpretable signals. A thermal camera captures an image using the heat difference emitted by objects in the infrared spectrum, and object detection in thermal images becomes effective for autonomous driving in challenging conditions. Although object detection in the visible spectrum domain has matured, thermal object detection lacks effectiveness. A significant challenge is the scarcity of labeled data for the thermal domain, which is essential for SOTA artificial intelligence techniques. This work proposes a domain adaptation framework that employs a style transfer technique for transfer learning from visible spectrum images to thermal images. The framework uses a generative adversarial network (GAN) to transfer the low- level features from the visible spectrum domain to the thermal domain through style consistency. The efficacy of the proposed object detection method in thermal images is evident from the improved results when using styled images from publicly available thermal image datasets (FLIR ADAS and KAIST Multi-Spectral).